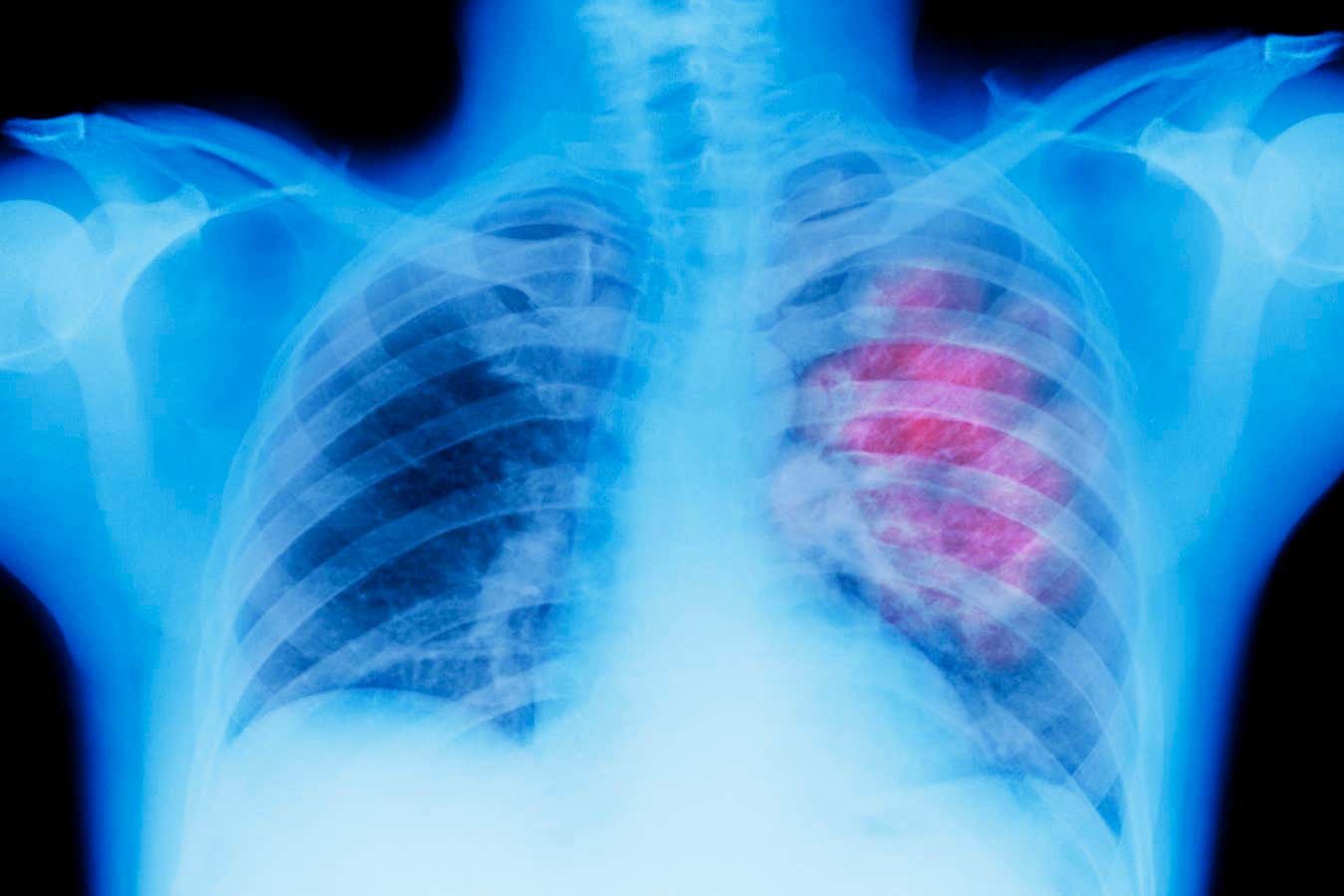
Medical artificial intelligence (AI) systems can diagnose diseases based on medical images, but they often struggle to determine when they might be incorrect. In an attempt to address this issue, Google has developed a new AI system that can determine when to trust AI-generated medical diagnoses and when to seek a second opinion from a human doctor. The system, called Complementarity-driven Deferral-to-Clinical Workflow (CoDoC), aims to improve the efficiency of analyzing medical scan data by reducing workload by 66%. However, it has yet to be tested in a real clinical environment.
CoDoC works by helping the predictive AI system recognize when it lacks knowledge or reliable answers. It is meant to be used in conjunction with existing AI systems that interpret medical images like X-rays and mammograms. For example, if an AI tool is analyzing a mammogram, CoDoC will determine if the tool’s perceived confidence is strong enough to rely on for a diagnosis or if a human should be involved in cases of uncertainty.
In a theoretical test conducted by Google Research and Google DeepMind, CoDoC reduced false positive interpretations of mammograms by 25%. The system was trained using data that included predictive AI tools’ analyses of medical images, as well as assessments of the tool’s confidence level compared to human clinician interpretations and post-analysis confirmations through biopsies or other methods.
According to Alan Karthikesalingam, a researcher at Google Health UK, when CoDoC is used together with an AI tool and a real radiologist’s outputs, the resulting accuracy is better than using either the person or the AI tool alone. The tests were repeated using different datasets for mammography and tuberculosis screening, with similar positive results. The interoperability of CoDoC with various proprietary AI systems is one of its advantages, according to Krishnamurthy “Dj” Dvijotham at Google DeepMind.
While this development is promising, Helen Salisbury, a researcher at the University of Oxford, states that mammograms and tuberculosis checks involve fewer variables than most diagnostic decisions. Expanding the use of AI to other applications will therefore pose challenges. Salisbury believes that adding machine learning to systems where there is no post-hoc influence over the black box outputs is a good idea, but whether it will bring AI closer to being used widely in routine healthcare remains uncertain.