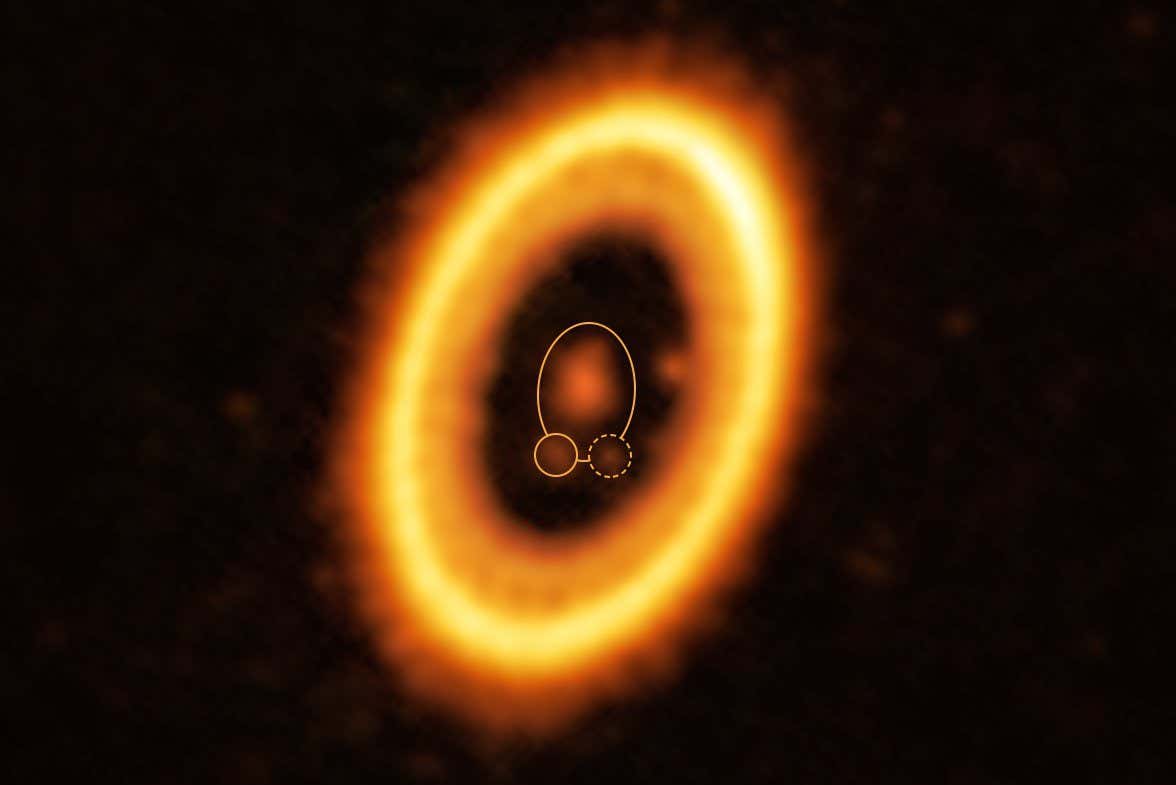The planetary system PDS features a star at its centre (in large white circle), orbited by the planet PDS 70b (in solid white circle) and a cloud of debris (in dotted white circle). Further out, the large yellow ring is a planet-forming circumstellar disc and there is another planet, PDS 70c, on its inner edge
ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO) /Balsalobre-Ruza et al.
Researchers have discovered two planets sharing an orbit in a star system located around 400 light years away. This is the first time ever that such a phenomenon has been observed. While asteroids co-orbiting with Jupiter, known as trojans, and some around Earth have been previously observed, these were believed to have been captured by the planets’ gravitational fields rather than forming in place.
Scientists, led by Álvaro Ribas at the University of Cambridge, have observed a dust cloud that appears to either be a forming planet or the remnants of a planet, sharing the same orbit as the gas giant exoplanet PDS 70b. PDS 70b itself is still in the early stages of formation. If confirmed, this discovery could suggest that trojans, such as asteroids, moons, and potentially even terrestrial planets, can form in situ.
Using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) in Chile, the research team studied PDS 70b’s Lagrangian points, which are gravitationally stable points where trojans could potentially exist. They found a ball of dust, similar in mass to Earth’s moon, composed of centimeter-sized rocks.
According to Matija Cuk at the SETI Institute in California, this is an extremely young system, and the orbital material is primordial, formed alongside the planet. The accumulation of dust and gas in the trojan point as the planet was growing is not something observed in our own solar system.
Confirmation of the second planet’s orbit and further insights into its composition will require additional observations in 2026 and technological upgrades to ALMA by 2030, respectively, as stated by Ribas.
However, even after acquiring more knowledge about this object, there remains the question of its classification. The International Astronomical Union (IAU) defines a planet as the only dominant mass in its gravitational district, referred to as “clearing the neighborhood.” Pluto was demoted to dwarf planet status since its moon Charon exerts its own gravitational influence. Ribas points out that if something forms at the Lagrangian point and possesses the mass of Earth, the IAU’s definition of a planet would conflict. Nevertheless, the IAU’s definition strictly applies to planets within the solar system, leaving the status of this newly discovered planet uncertain.
Topics: