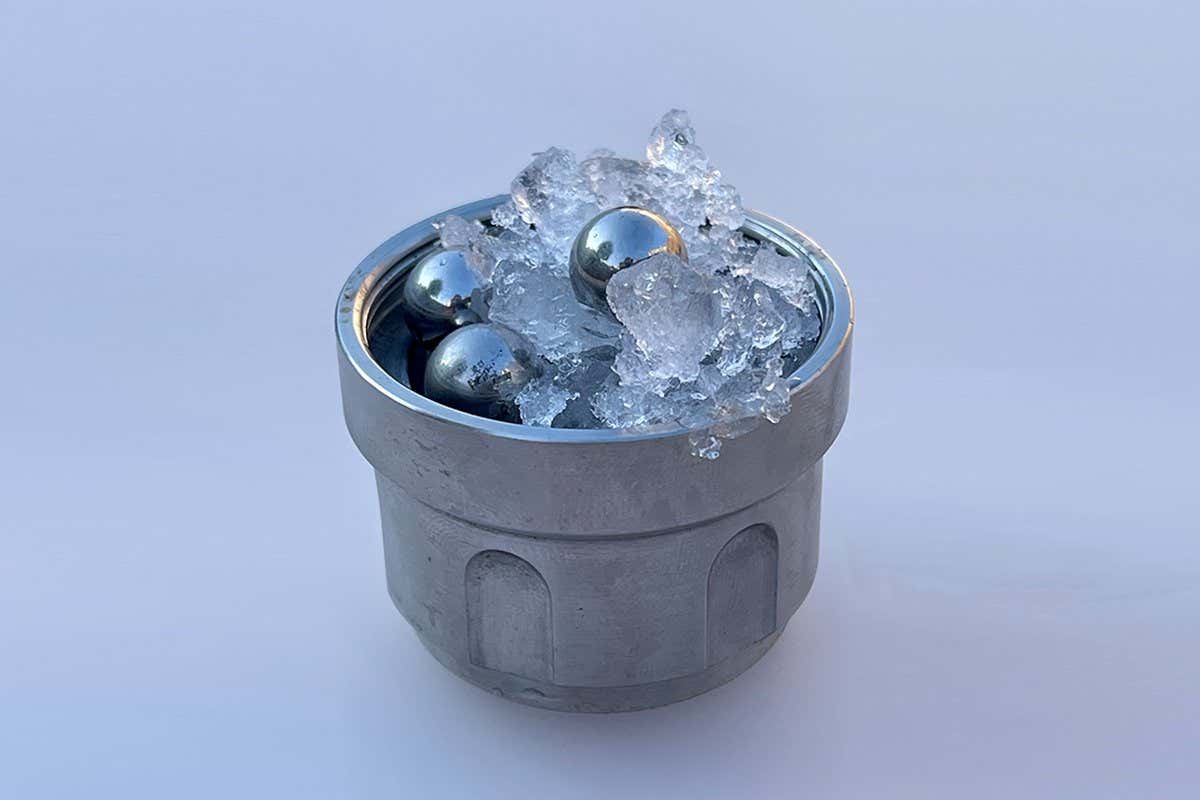
A new form of ice has been discovered by researchers which could help in understanding the mysteries of liquid water. This new ice is amorphous, meaning it does not have a neatly organized crystal structure. Previously, there were only two known types of amorphous ice – high-density and low-density. However, a team led by Christoph Salzmann at University College London accidentally created a new type of amorphous ice called medium-density amorphous ice (MDA) by putting regular ice into a tumbler with steel ball bearings cooled to -200°C (-328°F).
The researchers were surprised to find that the ice did not simply break down into smaller pieces but formed a fine white powder with a density similar to liquid water. This led them to suggest that the MDA may be water in a glass phase, which behaves like a liquid even at extremely low temperatures. Liquid water at very low temperatures is of great interest as it may exist in two different liquid phases simultaneously, a theory that MDA’s existence brings into question.
Understanding MDA could provide insights into the properties of liquid water. Researchers believe that MDA may also play a role in the icy moons of the outer solar system. These moons experience intense shear forces, and the conditions might be suitable for MDA to form. The researchers also discovered that when MDA was warmed up, it released an extraordinary amount of heat, which could have significant implications for the geological activity of these icy worlds.
Insights:
- The accidental discovery of medium-density amorphous ice (MDA) through an experiment involving regular ice and steel ball bearings cooled to -200°C (-328°F) could provide valuable insights into the properties of liquid water.
- MDA’s existence brings into question the theory that supercooled water can exist in two different liquid phases simultaneously.
- MDA may have implications for understanding the geological activity of icy moons in the outer solar system.
- When MDA is warmed up, it releases an extraordinary amount of heat.