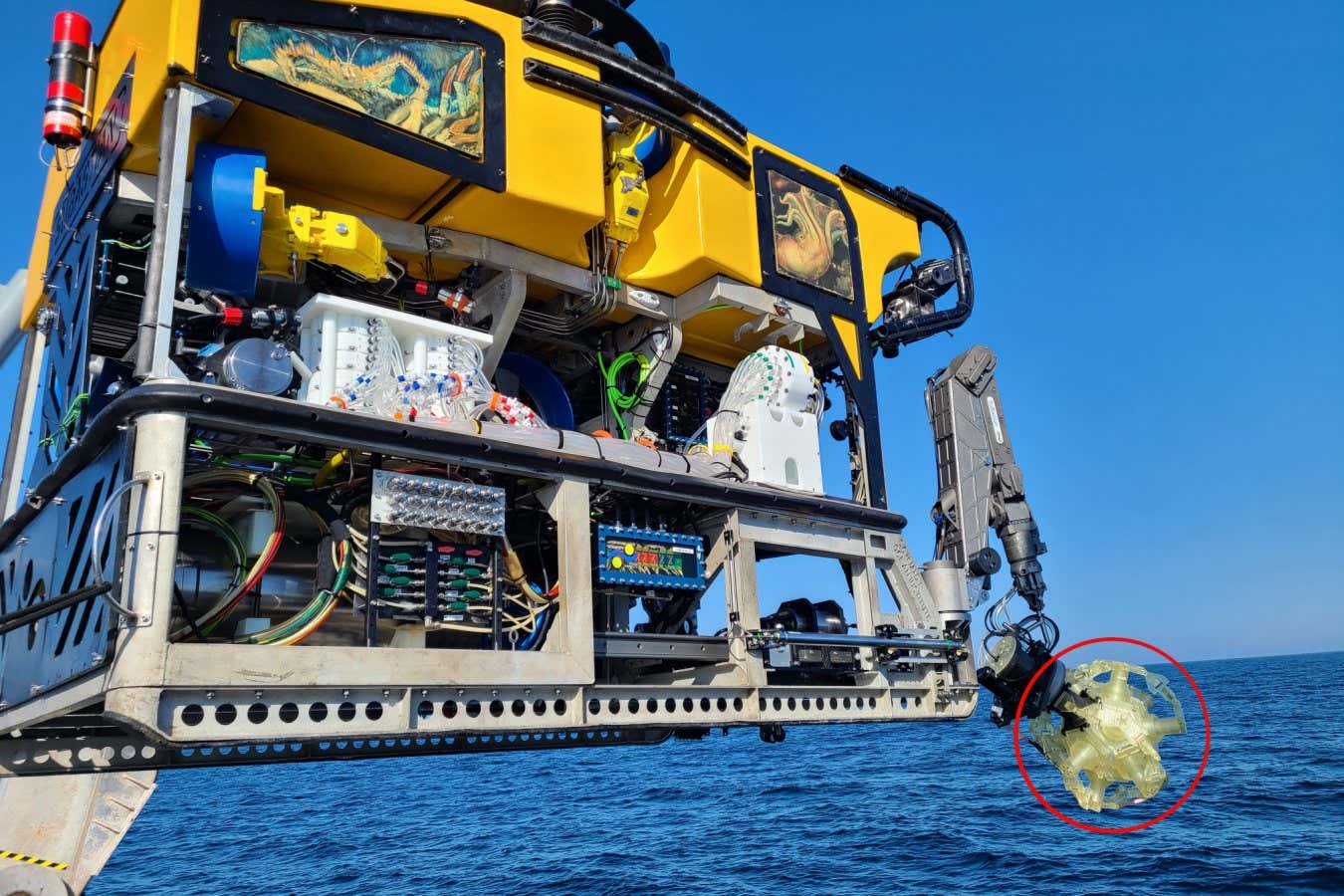
The robotic dodecahedron (circled) mounted on a submersibleBrennan Phillips
A robotic dodecahedron can seize fragile deep-sea animals to gather tissues samples and assemble three-dimensional scans of the creatures, probably dashing up the cataloguing of the as much as 66 per cent of ocean species which are but to be described by science.
Brennan Phillips on the College of Rhode Island and his colleagues developed the RAD2 sampler, designed to mount on any submersible, to gather contemporary tissue samples from residing animals in situ. They hope it will reveal extra in regards to the creatures than present strategies, which usually put them below stress as they’re hauled from the depths.
RAD2 is a dodecahedron with an inside quantity massive sufficient to carry a basketball. It’s designed to fold and unfold on command to quickly seize creatures for nearer examination, taking a small tissue pattern that’s preserved straight on the submersible for later genetic evaluation.
The final word intention is to take a small biopsy after which launch the animal comparatively unhurt, however RAD2’s present approach – referred to as tissue cleaving – is “a bit cruder”, says Phillips.
RAD2 has already been examined on two excursions, amassing as much as 14 tissue samples a day at depths of round 1200 metres. “We have been capable of get small items of tissue and generally we bought the entire animal,” he says. “It form of relied on how massive it was. So, I can’t go so far as claiming that we have been capable of launch the animal unhurt afterwards, however we’re transferring in direction of that.”
The robotic sampler additionally carries a 4K-resolution video digital camera to take high-quality footage of the animal in movement, whereas digital fashions of it are constructed by completely different 3D scanning units. Sooner or later, every of the dodecahedron’s 12 faces may comprise a sensor to take numerous measurements of the creature in a single go, says Phillips.
Phillips calls different sampling strategies “old fashioned”, saying they primarily contain manually placing issues in jars for later evaluation, or utilizing submersibles to do the identical.
With the preservation taking place on the level of assortment with RAD2, Phillips says the standard of tissue samples might be increased and even permit researchers to detect which genes are being expressed, probably shedding extra gentle on an animal’s behaviour and physiology. “That is the high-grade stuff,” he says. “That is one of the best you’re ever gonna get of this animal, higher than anyone has ever bought earlier than.”
Eva Stewart on the College of Southampton, UK, says that digital information on deep-sea creatures is usually a useful gizmo for analysis, however that there isn’t any substitute for capturing and storing entire samples.
“We have now 1000’s and 1000’s of kind specimens right here [at the university],” says Stewart. A few of them have been collected by the Swedish scientist Carl Linnaeus, she says, who died in 1778. “Individuals return to take a look at them, take bits of tissue or scan them. When you’ve bought a specimen, you’ve bought it. Whilst our science modifications, you may hold going again to it.”
However Stewart agrees that underwater scanning could possibly be helpful for gelatinous and different delicate animals, which will be exhausting to gather intact, and for understanding how creatures behave of their pure atmosphere, somewhat than after having been hauled onto the deck of a ship.
“We’ve been doing a little work genetic expression in sea cucumbers, as a result of we wish to see what they do after they’re pressured, in the event that they’re impacted by local weather change or one thing,” says Stewart. “However if you acquire them and produce them to the floor, that’s demanding. So getting the tissue from them extra naturally means you possibly can then probably look extra clearly at what occurs when they’re put in several circumstances as a result of what their pure baseline is.”
Matters: