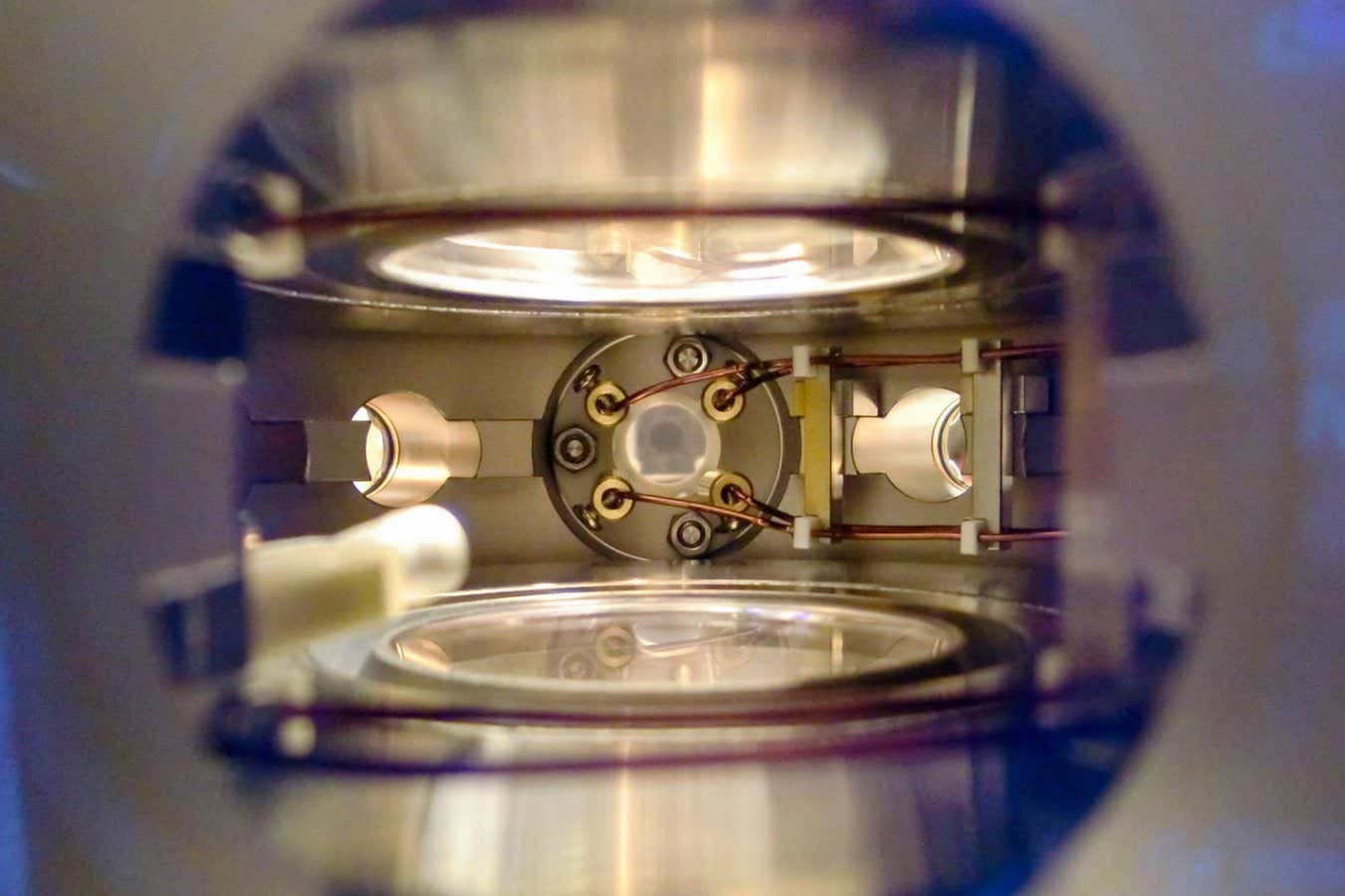
The vacuum chamber through which four-atom molecules have been cooled to just about absolute zero
Max Planck Institute of Quantum Optics
Molecules containing 4 atoms are the most important but to be cooled right down to solely 100 billionths of a level above absolute zero.
The methods researchers use for cooling particular person atoms, corresponding to hitting them with lasers and magnetic forces, don’t work as properly for molecules. That is very true for molecules made from many atoms, as a result of to be very chilly they should be very nonetheless – the extra transferring elements a molecule has, the extra alternatives it has to maneuver and heat up.
“We have now a joke that we research molecules not as a result of it’s simple, however as a result of it’s onerous,” says Xin-Yu Luo on the Max Planck Institute of Quantum Optics in Germany. He and his colleagues have now made four-atom molecules colder than ever earlier than.
They began with a number of thousand molecules composed of 1 sodium and one potassium atom, which they confined in an airless chamber and cooled – that’s, made very nonetheless – with magnetic forces and bursts of sunshine. The coldest potential temperature is 0 kelvin, or absolute zero; these molecules have been simply 97 billionths of a kelvin hotter.
To show these two-atom molecules into four-atom molecules, the researchers needed to mix them in pairs with out permitting them to heat up. They used microwave fields to “glue” molecules collectively primarily based on theoretical calculations by Tao Shi and Su Yi the Chinese language Academy of Sciences. “We actually didn’t know if we might assemble these molecules, however Tao’s crew did a calculation and he mentioned to me, ‘that is potential, simply strive it’,” says Luo.
Their trials have been profitable. The researchers created about 1100 molecules, every with two potassium and two sodium atoms, at a temperature of 134 billionths of a kelvin – the most important molecules to succeed in this ultracold temperature but.
“One of many causes you make molecules ultracold within the first place is to have extra management over them, and this can be a massive step ahead in that sense,” says John Bohn on the College of Colorado Boulder. The brand new experiment is vital not solely due to the molecules’ unprecedented temperature, but additionally as a result of at their coldest, they enter a recognized quantum state and might be pushed into one other state or a course of with precision, he says.
Luo says the atoms in these molecules should not “glued” to one another as strongly as these in room-temperature molecules. However making them is a needed step in the direction of finding out sophisticated chemical reactions, that are simpler to watch when they’re extraordinarily chilly and gradual.
The following query is what different, probably even larger molecules might be constructed at ultracold temperatures from equally frigid elements with an analogous microwave method, says Sebastian Will at Columbia College in New York. “I believe we’re thrilling new alternatives for quantum chemistry!” he says.
Subjects:
- chemistry /
- quantum physics