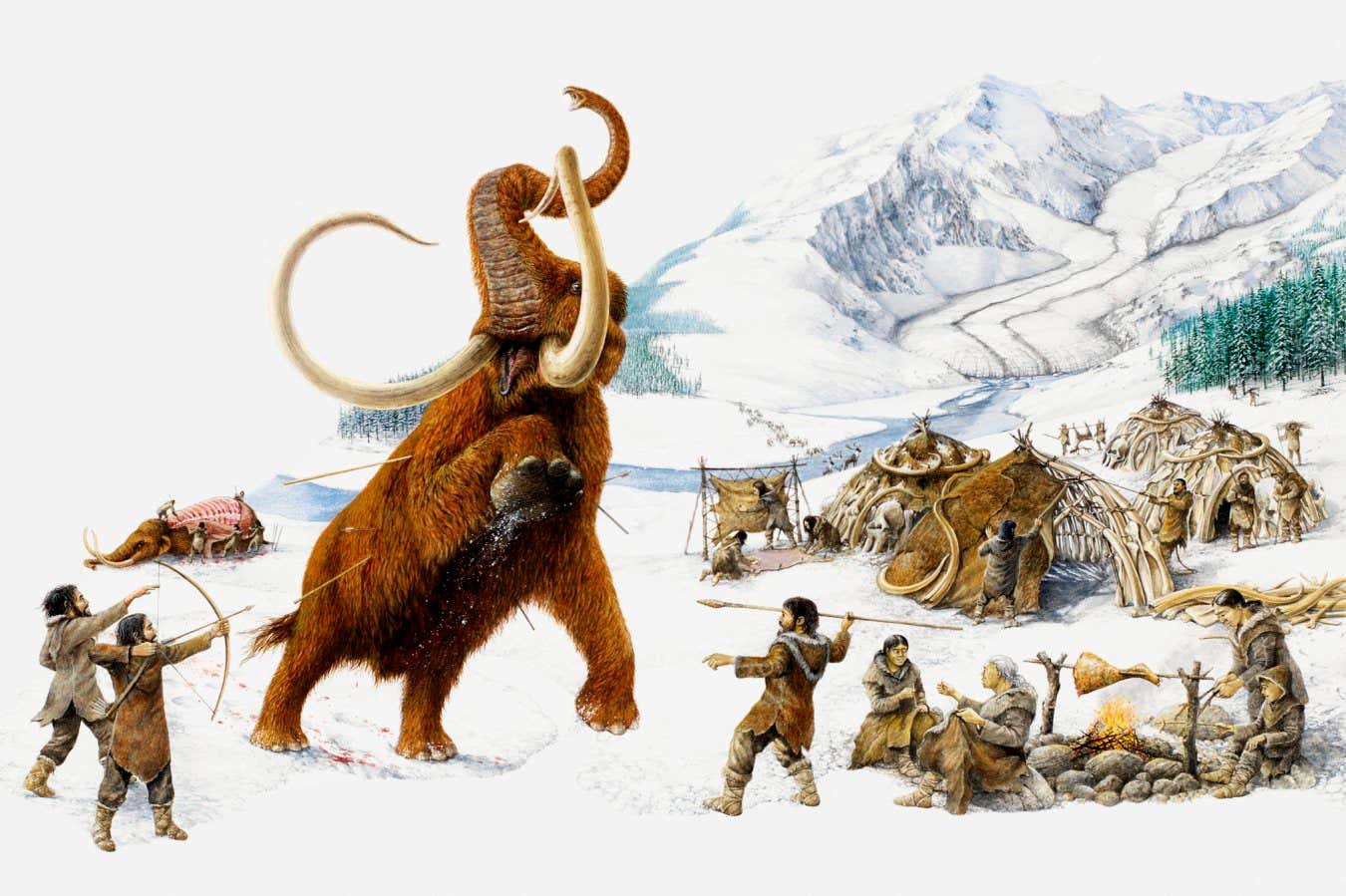
Early European people might have hunted mammoths in a frozen panorama
Dorling Kindersley/Getty Pictures
When fashionable people first started settling in Europe, they went straight to the chilly north. A difficult excavation in Germany locations our species within the area at the very least 45,000 years in the past – and helps earlier claims that our ancestors had been in Britain not lengthy after.
“These guys got here right into a panorama which was fairly hostile,” says Jean-Jacques Hublin on the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, Germany. “It was like northern Finland [today].”
Trendy people (Homo sapiens) are the newest hominin to completely settle in Europe, round 45,000 years in the past. Beforehand, the continent was dominated for lots of of 1000’s of years by Neanderthals, who vanish from the fossil file about 40,000 years in the past. Trendy people and Neanderthals might have overlapped in France and Spain for 1400 to 2900 years.
“The substitute of all archaic people by Homo sapiens, between 50,000 and 40,000 years in the past, is one thing that occurred throughout Eurasia,” says Hublin. It was a vital interval as a result of for tens of millions of years there had been a number of hominins coexisting, however now just one survived.
“That is the beginning of 1 species invading all of the doable liveable niches on the Earth,” says Hublin. “We all know it occurred… however we don’t know why and the way it occurred.”
The transitional period is mysterious. There are a number of varieties of stone artefacts from the interval that might have been made by Neanderthals or fashionable people. One, present in a number of websites in northern Europe, is the Lincombian-Ranisian-Jerzmanowician (LRJ) – characterised by lengthy, leaf-shaped factors which will have been fitted to spears. That they had by no means been present in affiliation with confidently recognized hominin bones. “We had no clue who made them,” says Hublin.
To search out out, Hublin and his colleagues visited a number of websites that had yielded LRJ artefacts. Sadly, earlier archaeologists had destroyed the websites with crude excavation strategies. The one exception was a cave known as Ilsenhöhle close to Ranis, Germany. It collapsed 1000’s of years in the past, so the preliminary excavations within the Thirties had been tough and among the website remained undisturbed. Hublin’s crew re-excavated it, digging a deep shaft right down to the related sediment layer.
So-called LRJ stone instruments discovered at Ilsenhöhle collapse Germany
Josephine Schubert, Museum Burg Ranis, (CC-BY-ND 4.0)
It was an “exceptionally tough” excavation, says Marie Soressi at Leiden College within the Netherlands, who wasn’t concerned within the examine.
Buried within the sediments, Hublin’s crew discovered many fragments of bone. Additionally they re-examined related fragments from the unique excavations. By analysing the collagen protein within the bones, they decided that 13 belonged to hominins. To determine them extra exactly, the crew extracted mitochondrial DNA, which individuals inherit solely from their moms, from 11 of the fragments. “They’re Homo sapiens,” says Hublin.
The strategies used had been “top-notch”, says Soressi. She desires to see nuclear DNA as effectively, to make certain, as a result of it’s doable the people had been hybrids with Neanderthal fathers – which mitochondrial DNA wouldn’t present. Nevertheless, she says that is “most unlikely”.
The timing of H. sapiens occupying the Ilsenhöhle matches with present proof. Hublin’s crew beforehand confirmed that fashionable people lived in Bacho Kiro collapse Bulgaria about 45,000 years in the past. Nevertheless, Ilsenhöhle is far additional north.
In a second examine, Hublin’s colleagues used chemical proof from preserved horse enamel to indicate that the local weather on this a part of Germany was chilly on the time, particularly between 45,000 and 43,000 years in the past. Once more, this matches prior proof: in 2014, Hublin’s crew confirmed that fashionable people had been residing in Willendorf, Austria, north of the Alps, in a chilly steppe-like surroundings 43,500 years ago.
A 3rd examine examines the animal bones from Ilsenhöhle, revealing that the cave was largely inhabited by cave bears and hyenas. The implication is that fashionable people had been solely there intermittently.
This factors to a “fast occupation by small teams of ‘pioneers’”, says Soressi.
Comparable claims have been made for the cave of Grotte Mandrin in France: it could have been briefly inhabited by fashionable people 54,000 years in the past, earlier than Neanderthals reclaimed the location.
Now that the LRJ instruments at Ilsenhöhle have been related to fashionable people, it’s affordable to imagine that different LRJ artefacts had been additionally made by H. sapiens, says Hublin. This means fashionable people made it to Britain early on. A part of a jawbone present in Kents Cavern in Devon, England, had been tentatively recognized as a contemporary human and dated to around 43,000 years ago – and was discovered with LRJ artefacts.
Matters:
- archaeology/
- historic people